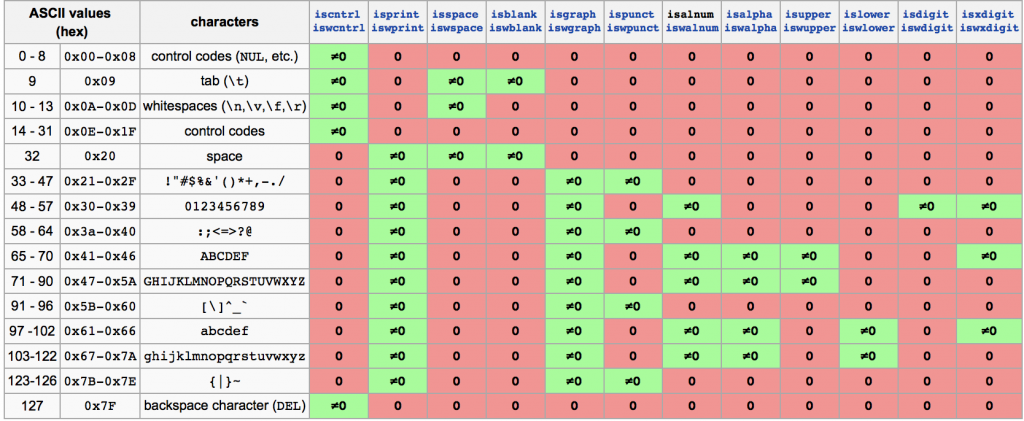
isalpha、islower、isupper、isalnum、isblank、isspace这些函数都在<cctype>的头文件里面,下图是它们所表示的范围:
总的来说就是:
你可不可以
成为我的main函数
做我此生必须有
且只能有一个的入口
——————————
我愿为自己加上private
在你的class中只有
你能调用
——————————————代 码 如 诗 。
isalpha、islower、isupper、isalnum、isblank、isspace这些函数都在<cctype>的头文件里面,下图是它们所表示的范围:

总的来说就是:
Given a string s and a non-empty string p, find all the start indices of p’s anagrams in s.
Strings consists of lowercase English letters only and the length of both strings s and p will not be larger than 20,100.
The order of output does not matter.
Example 1:
Input:
s: “cbaebabacd” p: “abc”
Output:
[0, 6]
Explanation:
The substring with start index = 0 is “cba”, which is an anagram of “abc”.
The substring with start index = 6 is “bac”, which is an anagram of “abc”.
Example 2:
Input:
s: “abab” p: “ab”
Output:
[0, 1, 2]
Explanation:
The substring with start index = 0 is “ab”, which is an anagram of “ab”.
The substring with start index = 1 is “ba”, which is an anagram of “ab”.
The substring with start index = 2 is “ab”, which is an anagram of “ab”.
分析:先将p字符串的所有字母的个数标记在hash数组中。设p的字符串长度为lenp,那么从字符串s的第一位开始分别找lenp长度的字串标记temphash,比较temphash是否等于hash,如果等于说明是anagram字符串,push_back到vector里面,最后返回vector
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
class Solution { public: vector<int> findAnagrams(string s, string p) { vector<int> result, hash(26, 0); int lenp = p.length(), lens = s.length(); for(int i = 0; i < lenp; i++) { hash[p[i] - 'a']++; } for(int i = 0; i <= lens - lenp; i++) { vector<int> temphash(26, 0); for(int j = i; j < i + lenp; j++) temphash[s[j] - 'a']++; if(temphash == hash) result.push_back(i); } return result; } }; |
You have a total of n coins that you want to form in a staircase shape, where every k-th row must have exactly k coins.
Given n, find the total number of full staircase rows that can be formed.
n is a non-negative integer and fits within the range of a 32-bit signed integer.
Example 1:
n = 5
The coins can form the following rows:
¤
¤ ¤
¤ ¤
Because the 3rd row is incomplete, we return 2.
Example 2:
n = 8
The coins can form the following rows:
¤
¤ ¤
¤ ¤ ¤
¤ ¤
Because the 4th row is incomplete, we return 3.
分析:直接用公式一行代码就能解决
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
class Solution { public: int arrangeCoins(int n) { return (int)((sqrt(8 * (long)n + 1) - 1)/ 2); } }; |
Given n points in the plane that are all pairwise distinct, a “boomerang” is a tuple of points (i, j, k) such that the distance between i and j equals the distance between i and k (the order of the tuple matters).
Find the number of boomerangs. You may assume that n will be at most 500 and coordinates of points are all in the range [-10000, 10000] (inclusive).
Example:
Input:
[[0,0],[1,0],[2,0]]
Output:
2
Explanation:
The two boomerangs are [[1,0],[0,0],[2,0]] and [[1,0],[2,0],[0,0]]
分析:map(m[i] = j)用来存储点与点之间距离(其实是距离的平方,不影响结果)为i的个数j。对于某一点,距离它为i的个数若为j个,则能够构成的i,j,k这样的组数是j * (j – 1)个。每次累计得到的总结果即为所求~
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
class Solution { public: int numberOfBoomerangs(vector<pair<int, int>>& points) { int cnt = 0; for(int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) { map<int, int> m; int x1 = points[i].first, y1 = points[i].second; for(int j = 0; j < points.size(); j++) { if(j == i) continue; int x2 = points[j].first, y2 = points[j].second; int dis = (x1 - x2)*(x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2)*(y1 - y2); m[dis]++; } for(auto it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++) { cnt += it->second * (it->second - 1); } } return cnt; } }; |
Given an array of integers where 1 ≤ a[i] ≤ n (n = size of array), some elements appear twice and others appear once.
Find all the elements of [1, n] inclusive that do not appear in this array.
Could you do it without extra space and in O(n) runtime? You may assume the returned list does not count as extra space.
Example:
Input:
[4,3,2,7,8,2,3,1]
Output:
[5,6]
分析:hash[i]用来标记i是否在nums数组中出现过。然后将没有出现过的放入result数组中,返回result数组~~~
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
class Solution { public: vector<int> findDisappearedNumbers(vector<int>& nums) { vector<int> result; vector<bool> hash(nums.size() + 1, false); for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) { hash[nums[i]] = true; } for(int i = 1; i < hash.size(); i++) { if(hash[i] == false) result.push_back(i); } return result; } }; |
Given a non-empty string check if it can be constructed by taking a substring of it and appending multiple copies of the substring together. You may assume the given string consists of lowercase English letters only and its length will not exceed 10000.
Example 1:
Input: “abab”
Output: True
Explanation: It’s the substring “ab” twice.
Example 2:
Input: “aba”
Output: False
Example 3:
Input: “abcabcabcabc”
Output: True
Explanation: It’s the substring “abc” four times. (And the substring “abcabc” twice.)
分析:设字串长度为len,字符串长度为slen,len从1开始一直到slen / 2遍历,如果slen % len != 0肯定当前len不符合,直接continue;否则将每一个长度为len的字串取出到sub2,比较与sub1是否相等,如果所有的都相等说明满足条件,return true,如果到最后循环结束后依旧没有找到这样一个len满足条件,则return false
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
class Solution { public: bool repeatedSubstringPattern(string str) { int slen = str.length(); for(int len = 1; len <= slen / 2; len++) { if(slen % len != 0) continue; string sub1 = str.substr(0, len); int flag = 0; for(int i = len; i < slen; i += len) { string sub2 = str.substr(i, len); if(sub1 != sub2) { flag = 1; break; } } if(flag == 0) return true; } return false; } }; |