Sublime -> Preferences -> Settings – User
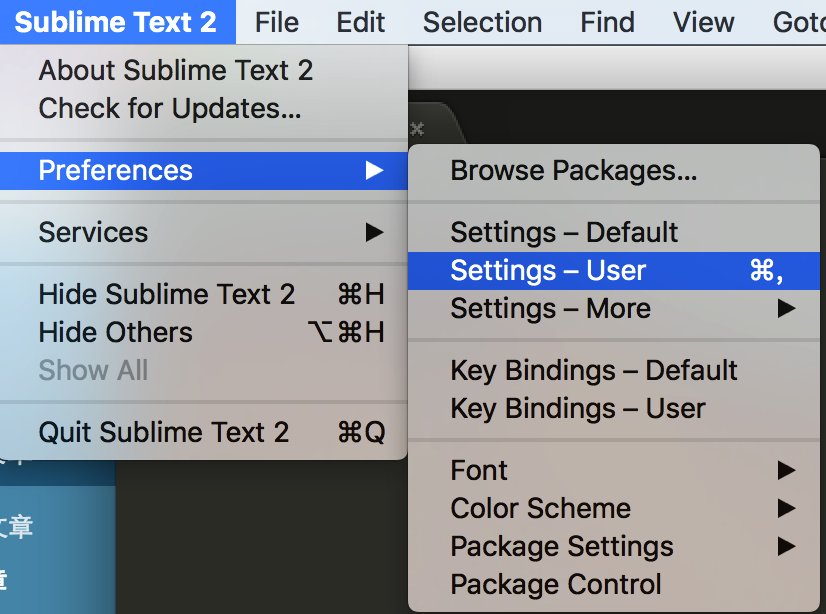
在里面添加一句 “word_wrap”: true
然后保存即可。
你可不可以
成为我的main函数
做我此生必须有
且只能有一个的入口
——————————
我愿为自己加上private
在你的class中只有
你能调用
——————————————代 码 如 诗 。
Sublime -> Preferences -> Settings – User

在里面添加一句 “word_wrap”: true
然后保存即可。

Sublime->Tools->Build System->New Build System…
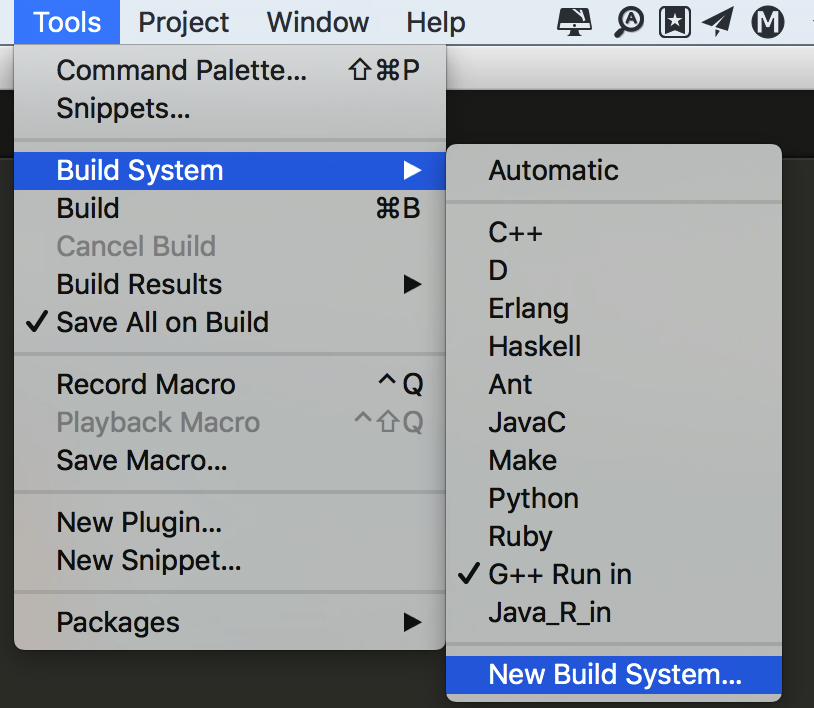
粘贴以下代码并保存为G++ Run in.sublime-build
|
1 2 3 |
{ "cmd": ["bash", "-c", "g++ '${file}' -o '${file_path}/${file_base_name}' && '${file_path}/${file_base_name}' < in"] } |
在要编译运行的cpp程序的文件夹下新建保存一个名为“in”的文件,作为接收输入数据的文件
然后在in文件里面输入输入数据并保存,打开需要编译运行的.cpp文件(要先保存为.cpp文件),按cmd+shift+B编译运行即可。
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is recursively defined as a binary tree which has the following properties:
The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than or equal to the node’s key.
The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node’s key.
Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Insert a sequence of numbers into an initially empty binary search tree. Then you are supposed to count the total number of nodes in the lowest 2 levels of the resulting tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (<=1000) which is the size of the input sequence. Then given in the next line are the N integers in [-1000 1000] which are supposed to be inserted into an initially empty binary search tree.
Output Specification:
For each case, print in one line the numbers of nodes in the lowest 2 levels of the resulting tree in the format:
n1 + n2 = n
where n1 is the number of nodes in the lowest level, n2 is that of the level above, and n is the sum.
Sample Input:
9
25 30 42 16 20 20 35 -5 28
Sample Output:
2 + 4 = 6
题目大意:输出一个二叉搜索树的最后两层结点个数a和b,以及他们的和c:“a + b = c”
分析:用链表存储,递归构建二叉搜索树,深度优先搜索,传入的参数为结点和当前结点的深度depth,如果当前结点为NULL就更新最大深度maxdepth的值并return,将每一层所对应的结点个数存储在数组num中,输出数组的最后两个的值~~
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 |
#include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; struct node { int v; struct node *left, *right; }; node* build(node *root, int v) { if(root == NULL) { root = new node(); root->v = v; root->left = root->right = NULL; } else if(v <= root->v) root->left = build(root->left, v); else root->right = build(root->right, v); return root; } vector<int> num(1000); int maxdepth = -1; void dfs(node *root, int depth) { if(root == NULL) { maxdepth = max(depth, maxdepth); return ; } num[depth]++; dfs(root->left, depth + 1); dfs(root->right, depth + 1); } int main() { int n, t; scanf("%d", &n); node *root = NULL; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { scanf("%d", &t); root = build(root, t); } dfs(root, 0); printf("%d + %d = %d", num[maxdepth-1], num[maxdepth-2], num[maxdepth-1] + num[maxdepth-2]); return 0; } |
Given a stack which can keep M numbers at most. Push N numbers in the order of 1, 2, 3, …, N and pop randomly. You are supposed to tell if a given sequence of numbers is a possible pop sequence of the stack. For example, if M is 5 and N is 7, we can obtain 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 from the stack, but not 3, 2, 1, 7, 5, 6, 4.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains 3 numbers (all no more than 1000): M (the maximum capacity of the stack), N (the length of push sequence), and K (the number of pop sequences to be checked). Then K lines follow, each contains a pop sequence of N numbers. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each pop sequence, print in one line “YES” if it is indeed a possible pop sequence of the stack, or “NO” if not.
Sample Input:
5 7 5
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
3 2 1 7 5 6 4
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
5 6 4 3 7 2 1
1 7 6 5 4 3 2
Sample Output:
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
题目大意:有个容量限制为m的栈,分别把1,2,3,…,n入栈,给出一个系列出栈顺序,问这些出栈顺序是否可能~
分析:按照要求进行模拟。先把输入的序列接收进数组v。然后按顺序1~n把数字进栈,每进入一个数字,判断有没有超过最大范围,超过了就break。如果没超过,设current = 1,从数组的第一个数字开始,看看是否与栈顶元素相等,while相等就一直弹出栈,不相等就继续按顺序把数字压入栈~~最后根据变量flag的bool值输出yes或者no~
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
#include <iostream> #include <stack> #include <vector> using namespace std; int main() { int m, n, k; scanf("%d %d %d", &m, &n, &k); for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) { bool flag = false; stack<int> s; vector<int> v(n + 1); for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) scanf("%d", &v[j]); int current = 1; for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { s.push(j); if(s.size() > m) break; while(!s.empty() && s.top() == v[current]) { s.pop(); current++; } } if(current == n + 1) flag = true; if(flag) printf("YES\n"); else printf("NO\n"); } return 0; } |
A family hierarchy is usually presented by a pedigree tree. Your job is to count those family members who have no child.
Input
Each input file contains one test case. Each case starts with a line containing 0 < N < 100, the number of nodes in a tree, and M (< N), the number of non-leaf nodes. Then M lines follow, each in the format:
ID K ID[1] ID[2] … ID[K]
where ID is a two-digit number representing a given non-leaf node, K is the number of its children, followed by a sequence of two-digit ID’s of its children. For the sake of simplicity, let us fix the root ID to be 01.
Output
For each test case, you are supposed to count those family members who have no child for every seniority level starting from the root. The numbers must be printed in a line, separated by a space, and there must be no extra space at the end of each line.
The sample case represents a tree with only 2 nodes, where 01 is the root and 02 is its only child. Hence on the root 01 level, there is 0 leaf node; and on the next level, there is 1 leaf node. Then we should output “0 1” in a line.
Sample Input
2 1
01 1 02
Sample Output
0 1
题目大意:给出一棵树,问每一层各有多少个叶子结点~
分析:可以用dfs也可以用bfs~如果用dfs,用二维数组保存每一个有孩子结点的结点以及他们的孩子结点,从根结点开始遍历,直到遇到叶子结点,就将当前层数depth的book[depth]++;标记第depth层拥有的叶子结点数,最后输出~
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; vector<int> v[100]; int book[100], maxdepth = -1; void dfs(int index, int depth) { if(v[index].size() == 0) { book[depth]++; maxdepth = max(maxdepth, depth); return ; } for(int i = 0; i < v[index].size(); i++) dfs(v[index][i], depth + 1); } int main() { int n, m, k, node, c; scanf("%d %d", &n, &m); for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) { scanf("%d %d",&node, &k); for(int j = 0; j < k; j++) { scanf("%d", &c); v[node].push_back(c); } } dfs(1, 0); printf("%d", book[0]); for(int i = 1; i <= maxdepth; i++) printf(" %d", book[i]); return 0; } |
A supply chain is a network of retailers(零售商), distributors(经销商), and suppliers(供应商)– everyone involved in moving a product from supplier to customer.
Starting from one root supplier, everyone on the chain buys products from one’s supplier in a price P and sell or distribute them in a price that is r% higher than P. Only the retailers will face the customers. It is assumed that each member in the supply chain has exactly one supplier except the root supplier, and there is no supply cycle.
Now given a supply chain, you are supposed to tell the lowest price a customer can expect from some retailers.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, The first line contains three positive numbers: N (<=105), the total number of the members in the supply chain (and hence their ID’s are numbered from 0 to N-1, and the root supplier’s ID is 0); P, the price given by the root supplier; and r, the percentage rate of price increment for each distributor or retailer. Then N lines follow, each describes a distributor or retailer in the following format:
Ki ID[1] ID[2] … ID[Ki]
where in the i-th line, Ki is the total number of distributors or retailers who receive products from supplier i, and is then followed by the ID’s of these distributors or retailers. Kj being 0 means that the j-th member is a retailer. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in one line the lowest price we can expect from some retailers, accurate up to 4 decimal places, and the number of retailers that sell at the lowest price. There must be one space between the two numbers. It is guaranteed that the all the prices will not exceed 1010.
Sample Input:
10 1.80 1.00
3 2 3 5
1 9
1 4
1 7
0
2 6 1
1 8
0
0
0
Sample Output:
1.8362 2
题目大意:提供一棵树,在树根处货物的价格为p,从根结点开始每往下一层,该层货物价格将会在父亲结点的价格上增加r%。求叶子结点出能获得的最低价格以及能提供最低价格的叶子结点数
分析:dfs。保存深度的最小值mindepth,以及最小值下该深度的个数minnum。深度优先搜索参数为index和depth,不断遍历index结点的孩子结点,直到当前结点没有孩子结点为止return~
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 |
#include <cstdio> #include <vector> #include <cmath> using namespace std; vector<int> v[100005]; int mindepth = 99999999, minnum = 1; void dfs(int index, int depth) { if(mindepth < depth) return ; if(v[index].size() == 0) { if(mindepth == depth) minnum++; else if(mindepth > depth) { mindepth = depth; minnum = 1; } } for(int i = 0; i < v[index].size(); i++) dfs(v[index][i], depth + 1); } int main() { int n, k, c; double p, r; scanf("%d %lf %lf", &n, &p, &r); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { scanf("%d", &k); for(int j = 0; j < k; j++) { scanf("%d", &c); v[i].push_back(c); } } dfs(0, 0); printf("%.4f %d", p * pow(1 + r/100, mindepth), minnum); return 0; } |