Given a non-empty tree with root R, and with weight Wi assigned to each tree node Ti. The weight of a path from R to L is defined to be the sum of the weights of all the nodes along the path from R to any leaf node L.
Now given any weighted tree, you are supposed to find all the paths with their weights equal to a given number. For example, let’s consider the tree showed in Figure 1: for each node, the upper number is the node ID which is a two-digit number, and the lower number is the weight of that node. Suppose that the given number is 24, then there exists 4 different paths which have the same given weight: {10 5 2 7}, {10 4 10}, {10 3 3 6 2} and {10 3 3 6 2}, which correspond to the red edges in Figure 1.
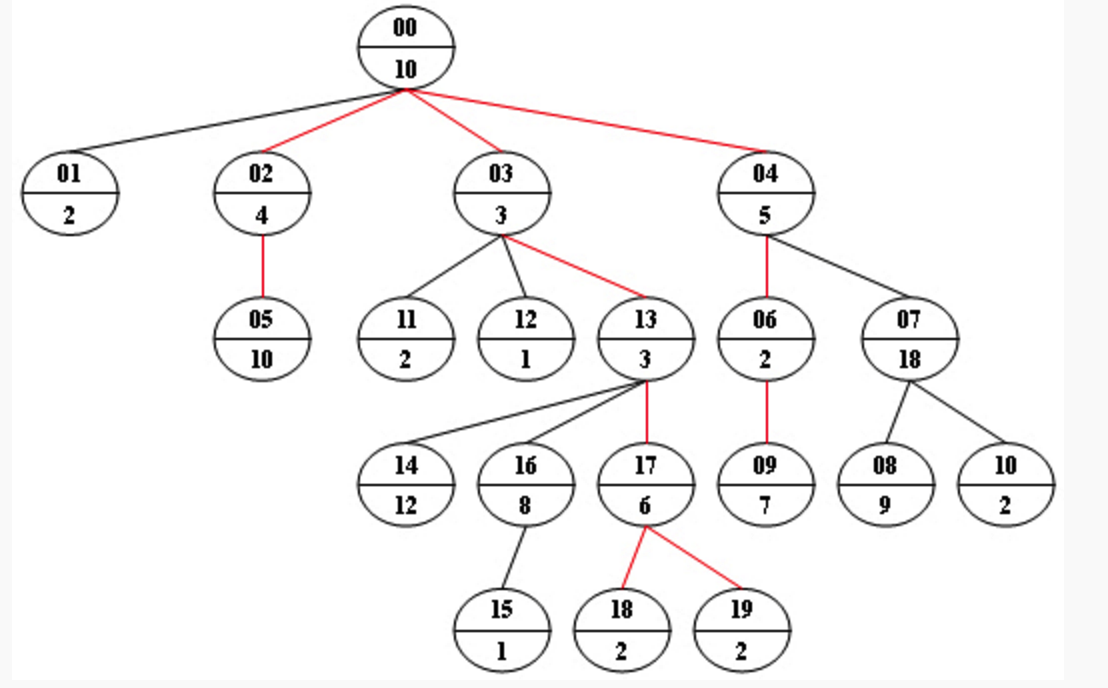
Figure 1
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case starts with a line containing 0 < N <= 100, the number of nodes in a tree, M (< N), the number of non-leaf nodes, and 0 < S < 230, the given weight number. The next line contains N positive numbers where Wi (<1000) corresponds to the tree node Ti. Then M lines follow, each in the format:
ID K ID[1] ID[2] … ID[K]
where ID is a two-digit number representing a given non-leaf node, K is the number of its children, followed by a sequence of two-digit ID’s of its children. For the sake of simplicity, let us fix the root ID to be 00.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print all the paths with weight S in non-increasing order. Each path occupies a line with printed weights from the root to the leaf in order. All the numbers must be separated by a space with no extra space at the end of the line.
Note: sequence {A1, A2, …, An} is said to be greater than sequence {B1, B2, …, Bm} if there exists 1 <= k < min{n, m} such that Ai = Bi for i=1, … k, and Ak+1 > Bk+1.
Sample Input:
20 9 24
10 2 4 3 5 10 2 18 9 7 2 2 1 3 12 1 8 6 2 2
00 4 01 02 03 04
02 1 05
04 2 06 07
03 3 11 12 13
06 1 09
07 2 08 10
16 1 15
13 3 14 16 17
17 2 18 19
Sample Output:
10 5 2 7
10 4 10
10 3 3 6 2
10 3 3 6 2
题目大意:给出树的结构和权值,找从根结点到叶子结点的路径上的权值相加之和等于给定目标数的路径,并且从大到小输出路径
分析:对于接收孩子结点的数据时,每次完全接收完就对孩子结点按照权值进行排序(序号变,根据权值变),这样保证深度优先遍历的时候直接输出就能输出从大到小的顺序。记录路径采取这样的方式:首先建立一个path数组,传入一个nodeNum记录对当前路径来说这是第几个结点(这样直接在path[nodeNum]里面存储当前结点的孩子结点的序号,这样可以保证在先判断return的时候,path是从0~numNum-1的值确实是要求的路径结点)。然后每次要遍历下一个孩子结点的之前,令path[nodeNum] = 孩子结点的序号,这样就保证了在return的时候当前path里面从0~nodeNum-1的值就是要输出的路径的结点序号,输出这个序号的权值即可,直接在return语句里面输出。
注意:当sum==target的时候,记得判断是否孩子结点是空,要不然如果不空说明没有到底部,就直接return而不是输出路径。。。(这对接下来的孩子结点都是正数才有用,负权无用)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 |
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; int target; struct NODE { int w; vector<int> child; }; vector<NODE> v; vector<int> path; void dfs(int index, int nodeNum, int sum) { if(sum > target) return ; if(sum == target) { if(v[index].child.size() != 0) return; for(int i = 0; i < nodeNum; i++) printf("%d%c", v[path[i]].w, i != nodeNum - 1 ? ' ' : '\n'); return ; } for(int i = 0; i < v[index].child.size(); i++) { int node = v[index].child[i]; path[nodeNum] = node; dfs(node, nodeNum + 1, sum + v[node].w); } } int cmp1(int a, int b) { return v[a].w > v[b].w; } int main() { int n, m, node, k; scanf("%d %d %d", &n, &m, &target); v.resize(n), path.resize(n); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) scanf("%d", &v[i].w); for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) { scanf("%d %d", &node, &k); v[node].child.resize(k); for(int j = 0; j < k; j++) scanf("%d", &v[node].child[j]); sort(v[node].child.begin(), v[node].child.end(), cmp1); } dfs(0, 1, v[0].w); return 0; } |
